Grouping-think
According to a recent press release ("Scientists Have Established a Key Biological Difference Between Psychopaths and Normal People"),
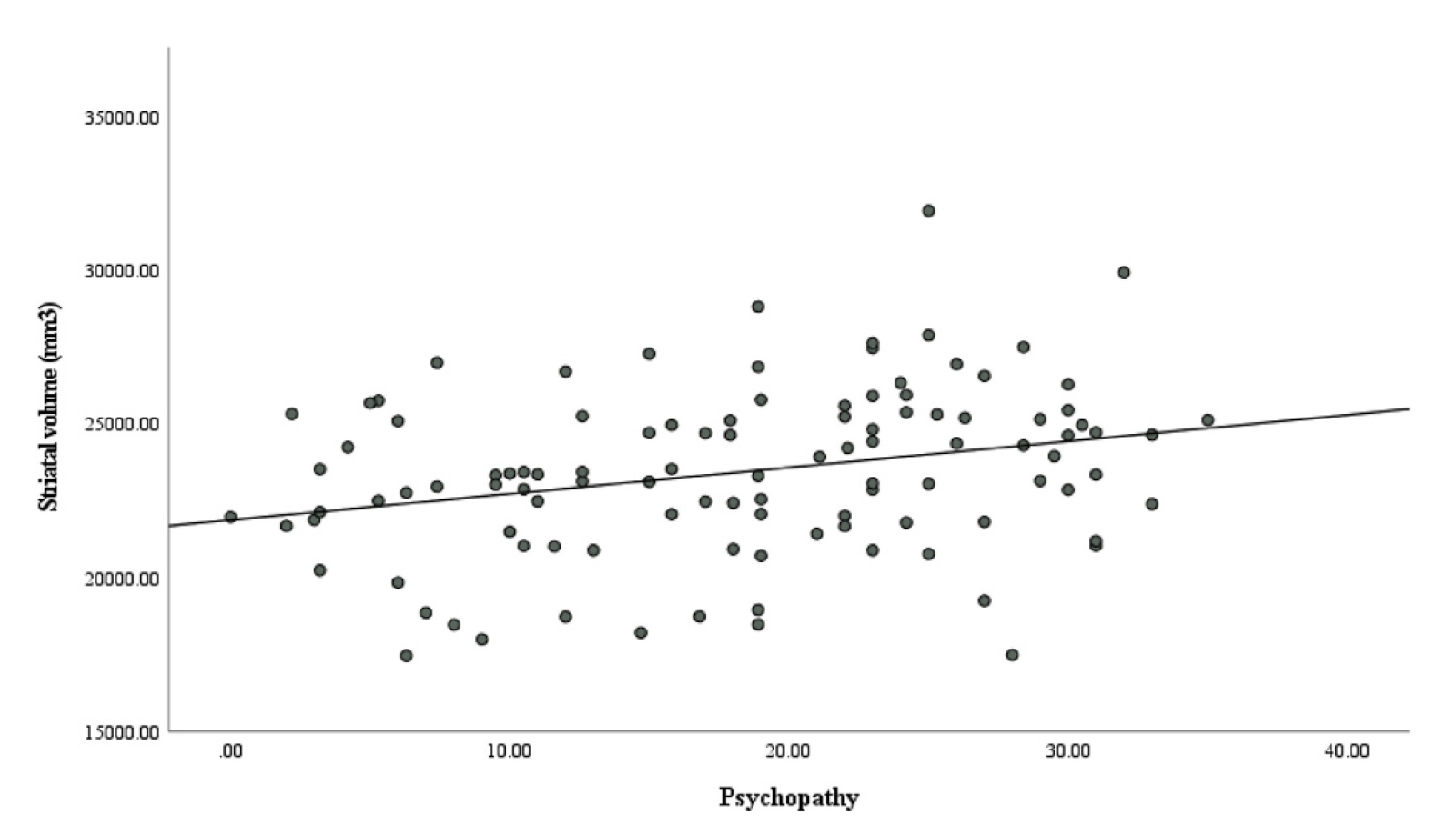
Neuroscientists using MRI scans discovered that psychopathic people have a 10% larger striatum, a cluster of neurons in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain, than regular people. This represents a clear biological distinction between psychopaths and non-psychopathic people.
The journal article (Choy et al., "Larger striatal volume is associated with increased adult psychopathy”) tells us that "Psychopathy was assessed using the PCL-R, which consists of 20 items rated by interviewers on a 3-point scale". (Wikipedia on PCL-R here). And from MRI scans, "segmentation of the caudate, putamen, nucleus accumbens, and globus pallidus was conducted together with the thalamus and cerebellum using standard FreeSurfer parcellation. Total striatal volumes were defined as the sum of the volumes of the four striatal subregions".
The generic plural "psychopaths" suggests a natural kind. And the phrase "a clear biological distinction" suggests well-defined and well-separated clusters of values on both neuro-anatomical and social-psychological dimensions. But what the researchers found was two weakly-correlated variables ("psychopathy" and "striatal volume"), each an amalgam of several measurements or evaluations, without any strong indication of clustering. Their Figure 3 (n=108):
Read the rest of this entry »